- What is PGT-A +
- Who can BENEFIT +
- Benefits of PGT-A +
- PGT-A results +
- How does PGT-A work +
- FAQ +
- References +
- Embryo Cost Calculator +
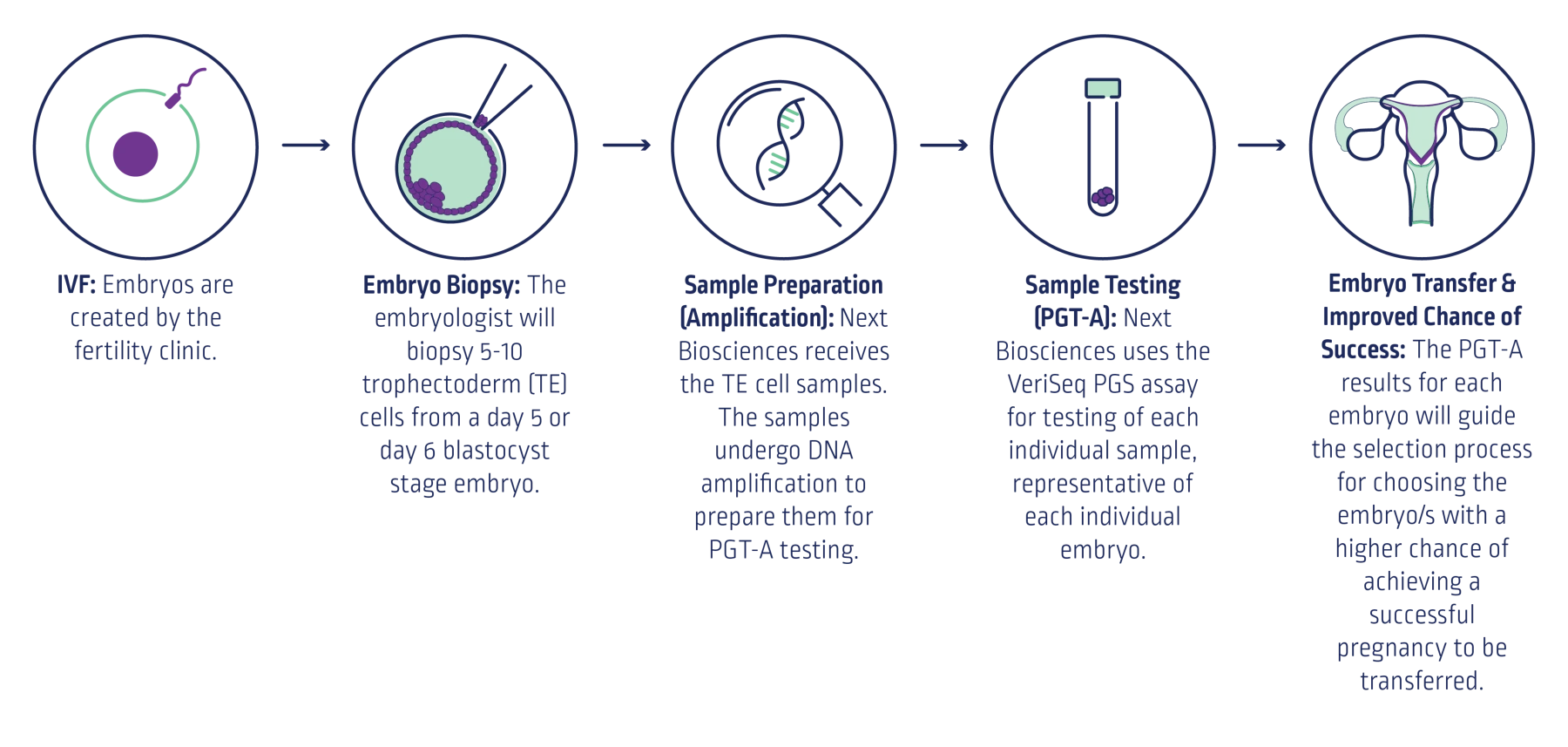
Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) is a genetic test that can be performed on embryos produced through IVF to screen for chromosomal abnormalities.
The term 'preimplantation' is used because testing is performed on embryos during the time before they would naturally implant into the uterus (usually after day 6). PGT-A is offered as a complement to a patient’s in vitro fertilisation (IVF) treatment.
PGT-A offered by Next Biosciences aims to improve pregnancy success rates and reduce the risk of miscarriage by avoiding the transfer of embryos with the incorrect number of chromosomes.
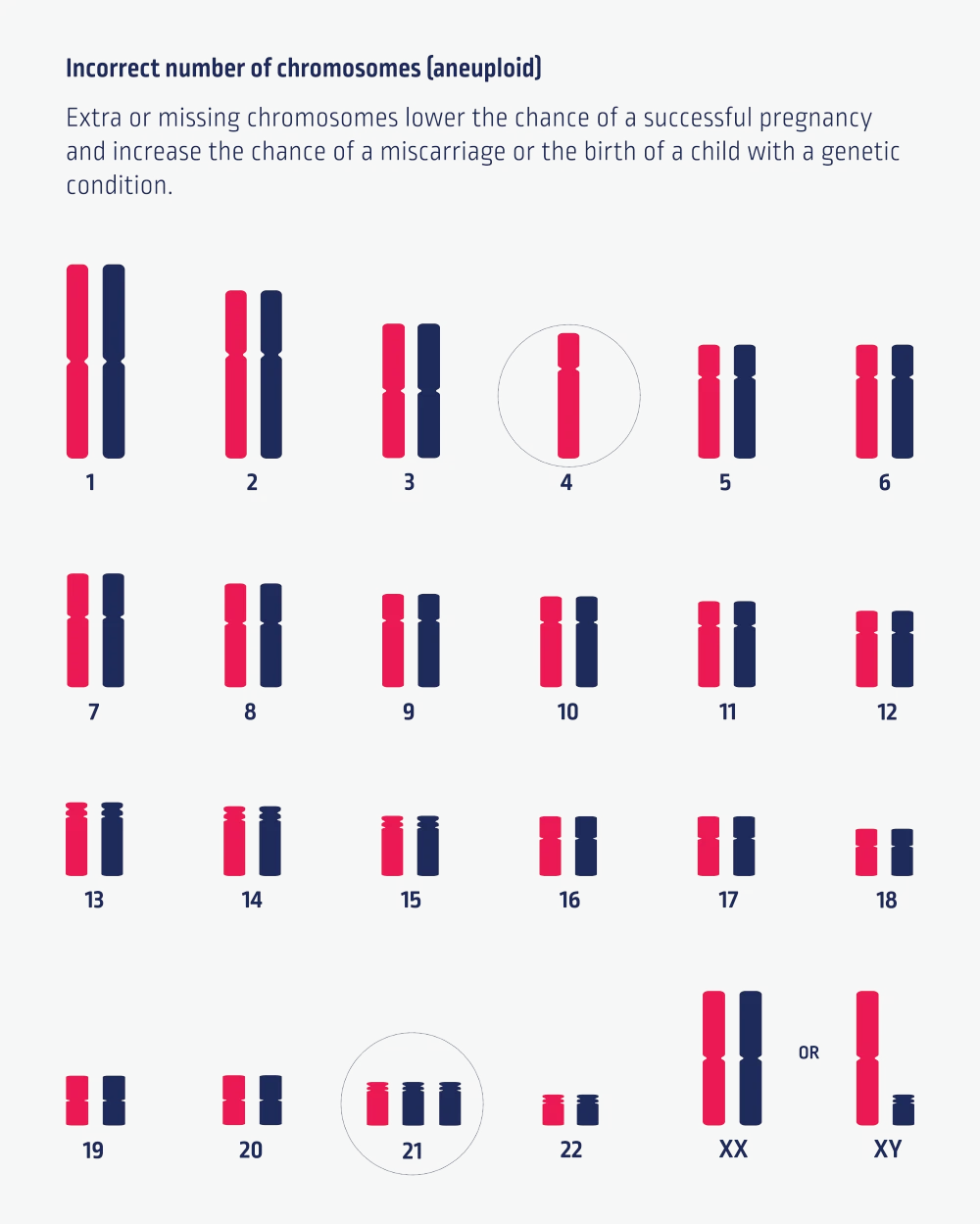
What is a chromosomal abnormality?
Humans typically have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 in total) within almost every cell in our body. One chromosome of each pair comes from our mother, and the other from our father. The first chromosome pairs are labelled 1-22. The last pair of these chromosomes are the sex chromosomes, which determine if you are genetically male or genetically female. Individuals who are genetically female typically have two X chromosomes, while individuals who are genetically male typically have an X and a Y chromosome.
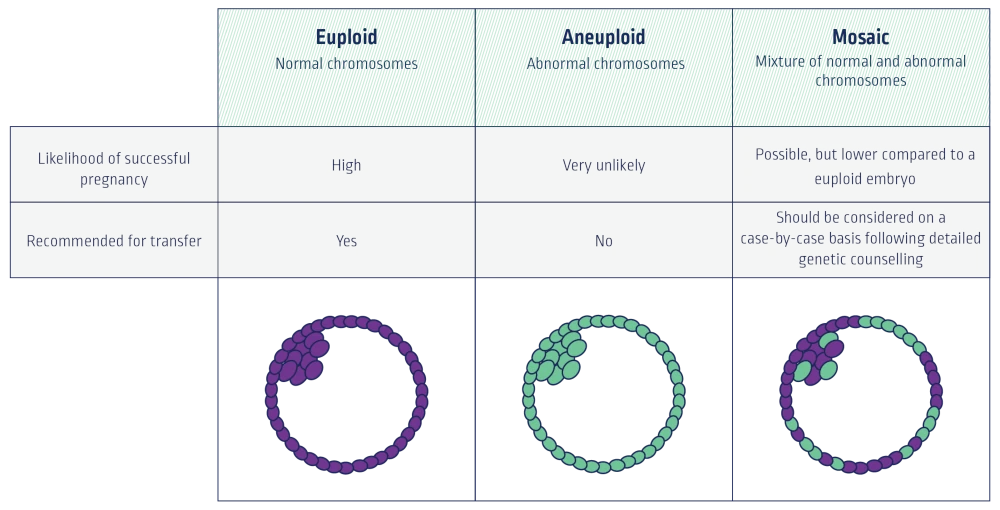
A change in the number of chromosomes can lead to a change in development. Embryos with the incorrect number of chromosomes are unlikely to lead to a successful pregnancy, may end in a miscarriage, or may result in the birth of a child with a genetic condition.
Embryos with the correct number of chromosomes are more likely to lead to a successful pregnancy.

PGT-A is available to any patient, but is typically prescribed for1,2:
- Couples where the female patient is of advanced maternal age (35 years or older)
- Patients who have experienced recurrent pregnancy losses both naturally and/or through IVF
- Patients who have experienced recurrent implantation failure
- Couples where severe male factor infertility has been identified
Is PGT-A safe?
Yes, scientific studies have shown that embryo biopsies do not add risk factors to the health of babies born after IVF.
How do I know if PGT-A will be beneficial for me?
If you are interested in PGT-A, talk to your fertility doctor to see if it's a good testing option for you, as PGT-A might not be right for everyone.
Pre-test genetic counselling is advised. Next Biosciences has an in-house genetic counsellor who can assist, or we can advise on other genetic counsellors who are experienced in PGT.
A genetic counselling session will ensure you fully understand the risks, benefits, and limitations of testing in your unique situation. While there are certain groups of patients that PGT-A will provide the most for, a genetic counsellor can help you better understand the possible outcomes of testing and whether there would be other benefits or limitations for you specifically.
Where are my embryos stored while I wait for my PGT-A results?
Your embryos will remain safely at your fertility clinic throughout the process, where they are stored frozen. Only the biopsied samples are sent to the Next Biosciences laboratory.
Does Next Biosciences offer embryo and/or embryo biopsy sample storage?
Next Biosciences allows you the option to amplify DNA from each embryo sample and keep this stored in the Next Biosciences laboratory for possible future testing. There is a once off cost for doing so, no annual storage fees apply. We do not offer embryo storage as embryos are routinely vitrified (frozen) and stored at fertility clinics.
How long will it take for my PGT-A results?
Provided we have received your signed Test Requisition Form (TRF) and payment for testing, results take 2 weeks from the day we receive the samples at the Next Biosciences laboratory. Next Biosciences will only release results to your doctor. Your doctor will then discuss the results with you.
Can PGT-A cause damage to my embryo/s?
There is a small risk of the biopsy procedure damaging the embryo, but this risk is minimal when performed by a suitably trained and experienced embryologist. The embryo will also need to be vitrified (frozen) while testing is underway, and then thawed prior to embryo transfer, which poses an additional but very small risk. You are encouraged to discuss these risks with your fertility clinic who will be able to share their own statistics with you.
Do normal PGT-A results mean that the embryo is normal?
No test can guarantee that a baby will not have any medical issues. PGT-A does not test for all genetic and non-genetic problems that may be present in a baby. Genetic counselling is recommended.
Do medical aids cover the cost of PGT-A?
No, unfortunately medical aids do not currently cover PGT-A.
- ESHRE PGT Consortium Steering Committee, Carvalho F, Coonen E, et al. ESHRE PGT Consortium good practice recommendations for the organisation of PGT. Hum Reprod Open. 2020;2020(3):hoaa021. Published 2020 May 29. doi:10.1093/hropen/hoaa021.
- Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. The use of preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A): a committee opinion. Fertil Steril. 2018;109(3):429-436. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.01.002.
- Rubio C, Bellver J, Rodrigo L, et al. In vitro fertilization with preimplantation genetic diagnosis for aneuploidies in advanced maternal age: a randomized, controlled study. Fertil Steril. 2017;107(5):1122-1129. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.03.011.
- Anderson RE, Whitney JB, Schiewe MC. Clinical benefits of preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) for all in vitro fertilization treatment cycles. Eur J Med Genet. 2020;63(2):103731. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2019.103731.
- Gorodeckaja J, Neumann S, McCollin A, et al. High implantation and clinical pregnancy rates with single vitrified-warmed blastocyst transfer and optional aneuploidy testing for all patients [published online ahead of print, 2019 Jan 7]. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2019;1-12. doi:10.1080/14647273.2018.1551628.
- Tiegs AW, Tao X, Zhan Y, et al. A multicenter, prospective, blinded, nonselection study evaluating the predictive value of an aneuploid diagnosis using a targeted next-generation sequencing-based preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy assay and impact of biopsy [published online ahead of print, 2020 Aug 27]. Fertil Steril. 2020;S0015-0282(20)30711-1. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.07.052.
- Munné S, Kaplan B, Frattarelli JL, et al. Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy versus morphology as selection criteria for single frozen-thawed embryo transfer in good-prognosis patients: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):1071-1079.e7. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2019.07.1346.
Embryo Cost Calculator
* Courier fees of samples from the clinic to the lab are calculated separately on an ad-hoc basis & will be communicated to you by the client services team.
| Item | Qty | Unit Price | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Embryos | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Amplification/Storage | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Testing (Previously Stored) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Grand Total | 0 |
Next Biosciences
Ariane Avenue
International Business Gateway
Cnr. New Road and 6th Road
Midrand, South Africa
Office Hours
Monday - Thursday: 08h00 - 17h00
Friday: 08h00 - 16h00